Difference between insurance and assurance: A critical distinction often blurred, these seemingly similar concepts serve profoundly different purposes. Insurance safeguards against financial loss, while assurance builds trust and confidence. This exploration delves into the nuances of each, examining their mechanisms, applications, and the crucial differences that set them apart.
Insurance protects against unforeseen events, providing financial compensation for losses. Assurance, on the other hand, verifies the reliability and validity of information, processes, and systems. This comparison will highlight the contrasting roles they play in various aspects of modern life.
Introduction to Insurance and Assurance: Difference Between Insurance And Assurance
Insurance and assurance, while often confused, are distinct concepts. Think of insurance as a safety net for potential financial losses, while assurance is about confirming the quality and reliability of something. They both aim to offer some form of protection, but their underlying mechanisms and scopes are vastly different. Imagine buying a car; you’d get insurance to cover accidents, but assurance might confirm the car’s mechanical integrity.
Understanding the nuances separates these two important financial instruments.Understanding the difference between insurance and assurance is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Insurance protects you from known risks, while assurance guarantees the quality or trustworthiness of a particular product, service, or entity. This distinction allows you to allocate resources effectively, knowing exactly what you’re getting and the potential pitfalls involved.
Definitions of Insurance and Assurance
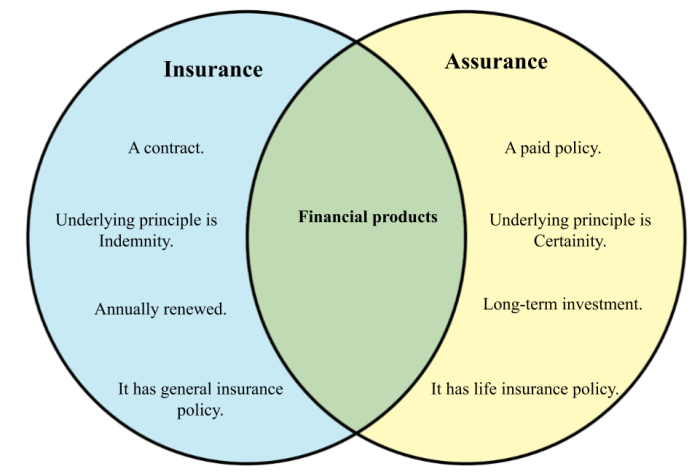
Insurance is a contract in which one party (the insurer) agrees to compensate another party (the insured) for losses or damages resulting from a specific event or risk. Essentially, it’s a mechanism for transferring financial risk from one party to another. This is often seen as protection against the unknown. A fire insurance policy, for example, covers losses from fire damage to a home.Assurance, on the other hand, is a confirmation of the quality, reliability, or trustworthiness of something.
It assures the user that the item meets a certain standard, a promise of quality. An independent audit report that confirms a company’s financial health is an example of assurance. It’s not about compensating for loss but guaranteeing a specific quality.
Fundamental Differences Between Insurance and Assurance
The key difference between insurance and assurance lies in their core purpose. Insurance is about financial protection against unforeseen events, whereas assurance is about guaranteeing the quality or reliability of something. One is about mitigating potential losses; the other is about confirming the quality. Insurance deals with risks, while assurance deals with facts. This is a fundamental and crucial distinction.
Comparison of Insurance and Assurance
| Characteristic | Insurance | Assurance | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Financial losses arising from specific events (e.g., accidents, illness, property damage) | Quality, reliability, or trustworthiness of a product, service, or entity | Insurance focuses on financial compensation for losses, while assurance focuses on confirming quality or reliability. |
| Purpose | To transfer financial risk from the insured to the insurer | To provide confidence in the quality or reliability of something | Insurance aims to protect against potential losses, while assurance aims to confirm the trustworthiness of a subject. |
| Mechanism | Contracts and premiums; claims process | Audits, certifications, and reports | Insurance uses contracts and premiums to transfer risk; assurance uses professional assessments and confirmations to validate quality. |
Insurance Mechanisms
Insurance, in essence, is a fascinating game of risk transfer. Imagine a world without it; you’d be solely responsible for any unforeseen calamity, from a broken pipe to a house fire. Insurance steps in, absorbing a portion of that risk, allowing you to sleep soundly knowing that someone else is holding the bag (or, rather, the policy). This risk-sharing mechanism is crucial for individual and societal well-being, enabling people to pursue their dreams and businesses without the constant fear of catastrophic financial loss.
Types of Insurance Policies
Insurance comes in a plethora of forms, each tailored to specific needs. Understanding the different types is paramount to selecting the right policy. Health insurance safeguards your well-being, covering medical expenses. Life insurance provides financial security for your loved ones after your departure. Property insurance protects your possessions, be it your house, car, or valuable items.
Each type operates on distinct principles and serves unique functions within the broader insurance landscape.
Principles Underlying Insurance Contracts
Insurance contracts, like any contract, are built on fundamental principles. These principles ensure fairness and transparency in the agreement. Utmost good faith (uberrima fides) is a cornerstone, requiring both parties to disclose all material information. Insurability is crucial, meaning the risk must be capable of being insured. Indemnity is another key principle, ensuring that the insured is restored to their pre-loss condition, not enriched.
Contribution is essential in cases where multiple policies cover the same loss, ensuring fair apportionment of costs.
Insurance Claims Process
The process of filing and settling an insurance claim can be a labyrinth, but following these steps usually leads to a smooth outcome. First, you’ll need to gather all necessary documentation, such as policy details, receipts, and supporting evidence. Next, you’ll report the claim to your insurance company, outlining the circumstances and the extent of the loss. The company will investigate the claim, potentially requiring further documentation or an assessment.
Once the claim is approved, the insurance company will provide the necessary compensation. This entire process aims to ensure that the insured is compensated fairly and efficiently.
Comparative Analysis of Insurance Products
Comparing different insurance products, such as health, life, and property insurance, is crucial for making informed decisions. Factors like coverage, premium structure, and claims process vary significantly. Health insurance, for instance, usually offers extensive coverage for medical treatments, while premiums depend on factors like age, location, and pre-existing conditions. Life insurance policies, in contrast, provide financial support to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death, with premiums based on factors like age and health status.
Property insurance protects assets from damage, with premiums varying depending on the value and location of the property. This comparative analysis highlights the tailored nature of insurance products to specific needs.
Key Elements of Different Insurance Policies
The following table Artikels the key elements of various insurance policies, offering a concise comparison.
| Policy Type | Coverage | Premium Structure | Claims Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health Insurance | Covers medical expenses, hospital stays, surgeries, and other treatments. Specific coverage varies by policy. | Premiums depend on factors like age, health status, location, and coverage options. Often have deductibles and co-pays. | Requires medical bills, doctor’s reports, and claim forms. Claims are processed based on policy terms and medical necessity. |
| Life Insurance | Provides a lump-sum payment to beneficiaries upon the death of the insured. Various types exist, such as term and whole life. | Premiums are determined by age, health, and the desired coverage amount. | Requires death certificate, policy documents, and beneficiary information. Claims are processed based on policy terms. |
| Property Insurance | Covers damage or loss to property due to various perils, such as fire, theft, or natural disasters. Covers the structure and contents. | Premiums are influenced by factors like property value, location, and the type of coverage desired. | Requires documentation of damage, photos, and police reports (if applicable). Claims are evaluated based on policy terms and the extent of the damage. |
Assurance Mechanisms
Assurance, unlike insurance, isn’t about covering risks. It’s about building trust. It’s about providing objective evidence that something meets predefined criteria. Think of it like a trusted friend verifying your work—not promising to pay if something goes wrong, but confirming its quality. Assurance services are crucial for businesses and individuals alike, ensuring confidence in everything from financial statements to product quality.Assurance engagements are designed to enhance trust and credibility by providing independent assessments of information or processes.
This independent assessment helps stakeholders make informed decisions. The process meticulously examines data, procedures, and controls to form an unbiased opinion.
Types of Assurance Services
Assurance services come in various flavors, each tailored to specific needs. Financial audits, for instance, delve into a company’s financial records to ensure accuracy and compliance. These audits scrutinize the entire financial picture, from revenues and expenses to assets and liabilities. Quality certifications, another example, verify that a product or service meets certain standards. These certifications assure customers that the product or service is of a specific quality.
These range from certifications for food safety to ISO standards for various industries. These assessments often involve on-site inspections, documentation reviews, and interviews.
Principles of Assurance Engagements
Assurance engagements are governed by several key principles. Professional skepticism, a cornerstone of assurance, involves a critical and questioning mindset throughout the engagement. This means independent professionals should not accept information at face value but instead scrutinize it thoroughly. Independence is another crucial principle. The assurance provider must remain unbiased and objective in their assessment.
This objectivity is essential for building trust. Competence is also vital, ensuring the assurance provider possesses the necessary skills and knowledge to perform the engagement effectively. Finally, due professional care is paramount, ensuring that the engagement is performed with the utmost diligence and attention to detail.
Procedures in Assurance Processes
The assurance process involves several crucial steps. Firstly, understanding the client’s needs and the objectives of the engagement is vital. This involves clearly defining the scope and limitations of the assurance work. Next, planning the engagement involves determining the procedures necessary to gather sufficient, appropriate evidence. This includes designing appropriate audit tests.
Gathering evidence is the heart of the process, using various methods such as examining records, observing procedures, and interviewing personnel. Evaluating the evidence is critical to form an opinion. Finally, communicating the findings and conclusions to the stakeholders is paramount, ensuring the opinion is clear, concise, and readily understandable.
Role of Independent Professionals
Independent professionals play a crucial role in assurance engagements. Their objectivity and expertise are essential to ensuring the reliability of the information being assessed. These professionals must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to maintain their credibility. They should be aware of and understand the standards applicable to their work. This includes industry-specific standards and professional codes of conduct.
Understanding the difference between insurance and assurance is key. Insurance, like a safety net, provides financial protection against unforeseen events. Conversely, assurance, more akin to a promise, guarantees a certain outcome. Finding affordable housing is a significant challenge for many, and securing suitable accommodations that accept Section 8 vouchers in Houston, TX, can be a real struggle.
Thankfully, resources like new apartments that accept section 8 vouchers in houston tx can help navigate this complex process. However, understanding the difference between insurance and assurance remains essential in navigating life’s various challenges. Ultimately, both concepts provide security and peace of mind in different ways.
Their role is to add credibility to the assessment and give confidence to the stakeholders.
Strengthening Trust and Confidence
Assurance services build trust and confidence in a variety of ways. By providing independent and objective assessments, assurance services reduce uncertainty and risk. This is particularly valuable for stakeholders who lack the time or expertise to evaluate the information themselves. This independent verification allows stakeholders to make informed decisions, leading to greater efficiency and effectiveness in their actions.
Understanding the difference ‘tween insurance and assurance is key, especially when considering a significant investment like a home. For example, searching for homes for sale in Beaver PA homes for sale in beaver pa requires careful consideration of both aspects. Insurance protects against unforeseen circumstances, while assurance is more about the reliability of the property’s condition.
Ultimately, knowing the nuances of each is crucial for a sound financial decision regarding any potential purchase.
Comparison of Assurance Services
| Assurance Type | Scope of Work | Output | Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Audits | Reviewing financial statements, internal controls, and transactions to ensure accuracy and compliance with regulations. | An independent opinion on the fairness of the financial statements. | Enhanced investor confidence, improved decision-making, and reduced risk of fraud. |
| Quality Certifications | Assessing the quality management systems and processes of an organization to meet specific standards (e.g., ISO 9001). | A certificate confirming the organization’s adherence to the standards. | Improved product quality, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased market competitiveness. |
Insurance vs. Assurance in Practice

Insurance and assurance, though both dealing with risk, are fundamentally different. Insurance is like a safety net, a financial cushion against unforeseen events. Assurance, on the other hand, is more about providing confidence and reliability. Think of it as the difference between buying a life insurance policy and getting a certified stamp of approval on a product’s quality.
Both play crucial roles in modern life, and understanding their practical applications in various sectors is key.
Real-World Examples of Insurance Applications
Insurance is ubiquitous. Imagine a small bakery. They might insure their equipment against fire damage, their liability against customer injuries, and their inventory against theft. In the manufacturing industry, large factories might have policies covering plant damage, worker compensation, and product defects. Even something as seemingly simple as a car requires insurance to cover potential accidents and damages.
These are just a few examples, highlighting the broad spectrum of risk insurance addresses.
Real-World Examples of Assurance Applications
Assurance is often less visible but just as critical. A financial institution might use assurance services to verify the accuracy of their financial statements, ensuring transparency and trust among investors. A software company might get assurance on the quality of their product, giving customers confidence in its reliability and functionality. Similarly, product safety assurance is crucial for consumer goods to build consumer trust and prevent harm.
Insurance and Assurance in Different Industries
Insurance and assurance play crucial roles across many industries. In the hospitality sector, hotels might insure against property damage and guest liability, while also seeking assurance regarding the quality of their services. Construction companies rely heavily on insurance covering project delays and accidents, and also need assurance regarding building compliance. The automotive industry relies on insurance for car accidents and warranties, and assurance for vehicle safety standards.
The key is understanding the unique risks in each industry and tailoring the appropriate insurance and assurance mechanisms.
Role of Insurance and Assurance in Risk Management
Insurance and assurance are powerful tools in risk management. Insurance mitigates financial losses associated with uncertain events, acting as a buffer against potential financial ruin. Assurance, on the other hand, helps identify and assess risks, ensuring that standards are met and reducing the likelihood of unforeseen issues. They work together to create a robust risk management strategy, allowing businesses and individuals to operate with greater confidence and stability.
Benefits of Insurance and Assurance
The benefits of insurance are clear – financial protection against unforeseen events. Assurance, however, provides a wider range of benefits, from increased trust and confidence to improved operational efficiency. A well-structured assurance program can prevent costly errors and delays, while also improving a company’s reputation and overall performance. The specific benefits depend on the context and nature of the application.
Limitations of Insurance and Assurance Mechanisms
No mechanism is perfect. Insurance policies have exclusions, meaning certain events are not covered. For instance, intentional damage might not be covered under a homeowner’s policy. Similarly, assurance procedures can only cover specific aspects of a process, not the entirety of the risk. Assurance reports are often based on past data, potentially failing to predict completely unforeseen events.
It’s crucial to recognize the limitations of each mechanism and tailor them to the specific needs and risks involved.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Insurance and assurance, while seemingly similar, have distinct legal and regulatory frameworks. Understanding these frameworks is crucial for anyone navigating these complex fields, because a misstep can lead to a lot of headaches and a significant impact on your bottom line. Think of it like navigating a maze; knowing the rules is the first step to getting where you need to be.
Legal Frameworks Governing Insurance Contracts
Insurance contracts, at their core, are legally binding agreements. These agreements are often complex, outlining the specific terms and conditions for coverage, compensation, and dispute resolution. They’re not just pieces of paper; they represent promises with legal consequences.
- Contractual Principles: Insurance contracts are governed by fundamental principles of contract law, including offer, acceptance, consideration, and capacity. These elements must be present for the contract to be valid and enforceable. Imagine it like a deal; both sides need to agree on the terms and give something of value in return.
- Specific Legal Requirements: Many jurisdictions have specific legal requirements for insurance policies. These often cover matters like policy wording, disclosure obligations, and the procedures for claims settlement. Think of it as a checklist; if any of these boxes aren’t ticked, the whole agreement could be in jeopardy.
- Statutory Regulations: Insurance is highly regulated at both the national and state levels. These regulations often address pricing, solvency, and claims handling. These rules are put in place to protect consumers and ensure the stability of the insurance industry. Think of it as a set of rules that the entire industry must follow.
Legal Frameworks Governing Assurance Engagements
Assurance engagements, while different from insurance, are also governed by legal frameworks. These frameworks often relate to the professional standards and ethical conduct of assurance providers.
- Professional Standards: Assurance providers, such as accountants or auditors, operate under professional standards that dictate the procedures and principles they must follow in conducting assurance engagements. These standards are crucial for maintaining objectivity and ensuring the quality of the assurance work. These standards are like the rules of the game for these professionals.
- Contractual Obligations: Assurance engagements are typically governed by contracts outlining the scope of work, fees, and deadlines. These contracts are legally binding and define the expectations for both the provider and the client. It’s a promise of service.
- Fraudulent Activities: Legal frameworks address fraudulent activities, including misrepresentation and falsification of information during assurance engagements. These rules help prevent and punish those who abuse the system. It’s like having a set of rules to catch those who try to cheat the system.
Regulatory Bodies Overseeing Insurance and Assurance Practices
Different regulatory bodies oversee insurance and assurance practices. This is done to maintain market stability, protect consumers, and ensure fair practices.
- Insurance Regulators: Insurance regulators ensure that insurance companies operate within legal and regulatory guidelines. They monitor financial stability, policy practices, and claims handling processes. Think of them as the referees of the insurance industry.
- Assurance Regulators: Assurance regulators, such as professional accounting bodies, oversee the professional conduct of assurance providers. They establish and enforce standards for audits, reviews, and other assurance services. These regulators act like the supervisors of the assurance profession.
Comparison of Legal Requirements for Insurance and Assurance Providers
While both insurance and assurance providers operate within legal frameworks, their specific requirements differ.
| Feature | Insurance Providers | Assurance Providers |
|---|---|---|
| Licensing | Generally require specific licenses to operate. | Often require professional certifications or memberships. |
| Capital Requirements | Often have stringent capital requirements to ensure solvency. | Capital requirements are less stringent, often related to professional standing. |
| Regulatory Oversight | Subject to extensive regulatory oversight, including financial reporting and solvency requirements. | Subject to oversight by professional bodies, focusing on professional standards and ethical conduct. |
Illustrative Cases
Insurance and assurance, two sides of the same coin, but with vastly different functions. Imagine a world without them – chaos! One protects you from financial losses, the other assures you of quality and reliability. Let’s dive into some real-world examples to see how they work in practice.
Insurance Case Study: The Flooded Factory
A small manufacturing plant, “Sunrise Ceramics,” produces exquisite pottery. Their factory, nestled in a flood-prone valley, suffered catastrophic damage during a torrential downpour. Their insurance policy, covering both property damage and business interruption, kicked in immediately. The insurance company facilitated the necessary repairs, and even provided temporary financial assistance to keep the business afloat while the factory was being rebuilt.
This exemplifies how insurance mitigates financial risk, providing a safety net against unforeseen disasters.
Assurance Case Study: The Certified Auditor
“Tech Titans,” a rapidly growing tech startup, needed to secure funding for expansion. They engaged an independent assurance firm to audit their financial statements. The assurance firm, after a thorough review, issued a clean audit opinion, assuring potential investors of the company’s financial health and stability. This report of financial integrity significantly influenced the investment decision, demonstrating assurance’s role in building trust and confidence in a company’s financial standing.
Comparison of the Two Case Studies
While both Sunrise Ceramics and Tech Titans faced critical situations, their solutions differed dramatically. Sunrise Ceramics used insurance to compensate for the tangible loss of property and income disruption, whereas Tech Titans used assurance to enhance investor confidence in their financial statements. Insurance focuses on replacing or compensating for financial losses, whereas assurance aims to build trust and reliability through independent verification.
Scenario for Insurance
Imagine a small farmer whose entire crop was destroyed by a hailstorm. Without insurance, the farmer would face devastating financial losses, potentially leading to the abandonment of their farm. Insurance provides a crucial safety net in this scenario, ensuring the farmer receives compensation for their loss and can continue their livelihood.
Scenario for Assurance
A company that provides a new type of software claims it significantly reduces energy consumption for businesses. To gain credibility and trust, the company needs to get an independent third-party assessment of the software’s effectiveness. This assessment, delivered by a reputable assurance provider, would demonstrate the validity of their claims, ultimately building confidence in the software’s capabilities and attracting potential clients.
Future Trends
The future of insurance and assurance is a fascinating, albeit somewhat blurry, landscape. Just like the ever-evolving world around us, these fields are poised for significant transformations, driven by technological advancements and shifting societal needs. From the rise of AI-powered risk assessments to the emergence of new types of assurance services, the next few years promise to be exciting, full of surprises, and potentially disruptive.
Potential Future Developments in Insurance
Insurance is a sector that’s rapidly adapting to the digital age. We’re likely to see a continued shift towards personalized insurance products, tailored to individual needs and risk profiles. Predictive modeling, powered by machine learning algorithms, will play a pivotal role in this. Imagine policies that adjust premiums based on your individual driving habits or even your lifestyle choices, all in real-time.
- Increased use of data analytics: Insurers will leverage vast datasets to predict and manage risks more effectively. This will result in more accurate premium calculations and a reduction in fraud.
- Emergence of new insurance products: The rise of emerging technologies, like self-driving cars and drones, will necessitate the development of innovative insurance products to address the associated risks. We’re already seeing this with cyber insurance and insurance for autonomous vehicles.
- Greater integration with technology: Expect a rise in mobile-first insurance platforms and seamless integration with other financial services. Imagine a single app to manage all your insurance needs.
Potential Future Developments in Assurance
Assurance, too, is on the cusp of significant change. The growing demand for transparency and accountability in various sectors will lead to an expansion of assurance services, encompassing areas beyond traditional financial reporting. Think about assurance for supply chain sustainability or the ethical sourcing of products.
- Shift towards broader assurance scopes: Assurance services will expand to encompass non-financial aspects of a business, such as environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Investors are increasingly interested in these factors, demanding assurance of their compliance and impact.
- Increased use of technology: Blockchain technology could play a crucial role in enhancing the transparency and immutability of assurance processes. This could streamline verification and reduce the risk of fraud.
- Focus on emerging technologies: The increasing complexity of software and digital ecosystems will necessitate specialized assurance services to verify their reliability and security. Think about assurance for the integrity of artificial intelligence systems or the security of data platforms.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements will be a driving force in reshaping both insurance and assurance. The advent of AI, machine learning, and blockchain technology is already transforming how these sectors operate. The ability to process massive amounts of data, predict risks more accurately, and streamline processes will lead to greater efficiency and cost savings.
- Enhanced risk assessment: AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and predict future risks more accurately. This leads to more tailored insurance products and proactive risk management strategies.
- Improved fraud detection: Machine learning models can identify fraudulent claims and activities with greater accuracy and speed. This reduces financial losses for insurers and improves customer trust.
- Increased automation: Automation of administrative tasks and claim processing can significantly reduce operational costs and improve efficiency for both insurers and assureds.
Role of Innovation in Shaping the Future, Difference between insurance and assurance
Innovation will be critical in navigating the future landscape of insurance and assurance. Insurers and assurance providers who embrace new technologies and adapt to changing customer needs will be better positioned for success. Companies that can develop innovative solutions to address emerging risks and provide value-added services will gain a competitive edge.
- Developing new solutions: Insurers and assurance providers must continuously develop new and innovative solutions to meet the evolving needs of customers and businesses.
- Adapting to technological changes: Keeping pace with technological advancements is essential to maintain competitiveness and provide relevant services. Embrace new tools and technologies to improve efficiency and efficacy.
- Investing in research and development: Investment in research and development will be crucial to stay ahead of the curve and discover innovative solutions to address future challenges.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the difference between insurance and assurance is vital for informed decision-making. Insurance mitigates financial risks, while assurance strengthens trust. By recognizing their distinct purposes and mechanisms, individuals and organizations can leverage both effectively to manage their needs and achieve their objectives. The key takeaway is that while both are crucial, they address fundamentally different aspects of our lives.
FAQ Section
What are some examples of assurance services?
Assurance services include audits, certifications (like ISO), and due diligence reviews. They aim to provide objective evidence about the reliability of information and processes.
How does insurance differ from risk assessment?
Insurance is a method of transferring risk to an insurer. Risk assessment, however, is about identifying and analyzing potential risks to determine their likelihood and impact.
Can assurance services be used in non-financial contexts?
Absolutely. Assurance services can be applied to various sectors like quality management, environmental sustainability, and even ethical practices.
What are the limitations of insurance?
Insurance policies often have exclusions and limitations. Some risks may not be insurable, and coverage is typically not unlimited.
